A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to identify and evaluate the internal Strengths and Weaknesses of an organization, as well as the external Opportunities and Threats it faces. As mentioned in a previous article, this tool is widely used by successful patient advocacy groups during the strategic planning process. Being part of this larger process can make SWOT analyses seem daunting, especially for individuals who have never conducted one. To address this, we have broken it down into its parts. In this article, we will be discussing the internal factors only (i.e., Strengths and Weaknesses).
At its core, a SWOT analysis differentiates between factors that are within the group’s control and those that are not (internal vs. external factors, respectively) and to identify if a factor is helpful or potentially harmful to the organization.
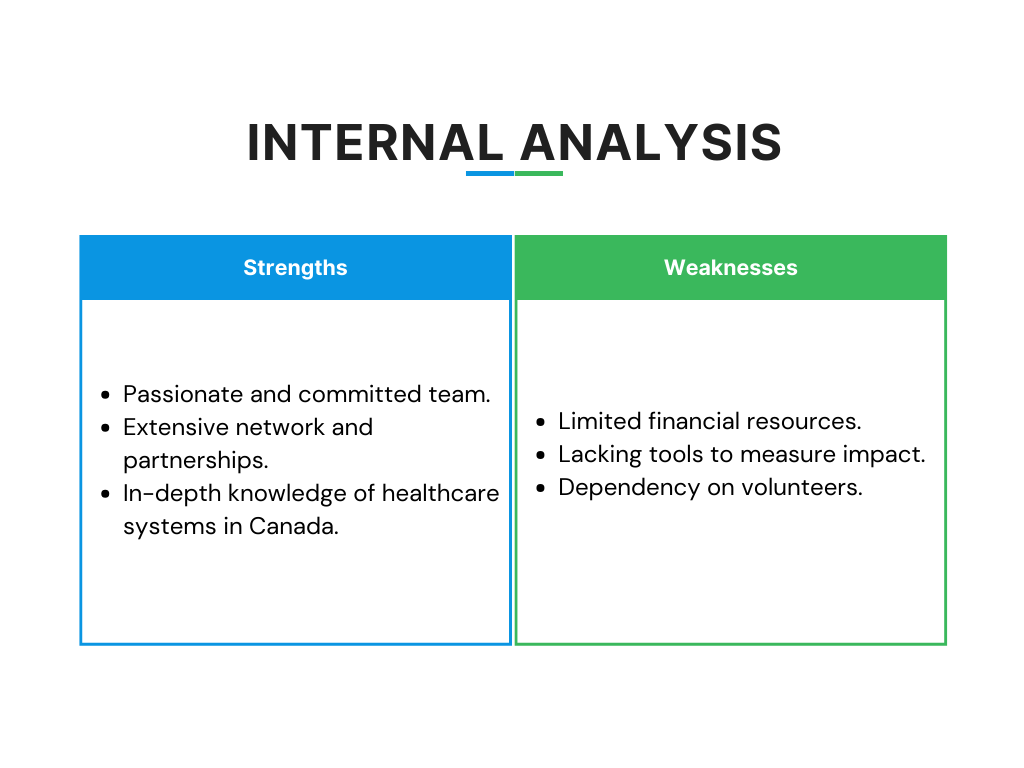
Strengths
Strengths are internal factors that help the organization have a competitive advantage or provide unique capabilities/services/products. These can include resources, expertise, skills, or any other internal positive attributes that contribute to the organization’s success.
Examples of Strengths that a patient advocacy group could include:
- Passionate and committed team.
- Context: the advocacy group has a dedicated team of volunteers who are passionate about advocating for patients’ rights and well-being.
- Extensive network and partnerships.
- Context: the group has established strong partnerships with healthcare providers and other stakeholders in the healthcare industry, which has in turn enhanced its ability to affect positive change in their disease area.
- In-depth knowledge of healthcare systems in Canada.
- Context: the entire team possesses a deep understanding of the Canadian healthcare system, including policies and regulatory bodies, which allows them to make more informed decisions regarding their advocacy efforts and better help their patient community navigate the system.
Weaknesses
Weaknesses are internal factors that put the organization at a disadvantage or represent areas where improvement is needed. These can include lack of resources, gaps in knowledge/expertise/skills, or any other internal negative attributes that may inhibit the success of the organization.
Examples of Weaknesses that a patient advocacy group could include:
- Limited financial resources.
- Context: the patient advocacy group is currently facing challenges due to limited funding, which is preventing large-scale campaigns and initiatives from being executed.
- Lacking tools to measure impact.
- Context: the patient advocacy group lacks tools to effectively measure the impact of advocacy efforts on patient outcomes; therefore, the group does not know if their limited resources are being used well.
- Dependency on volunteers.
- Context: the group relies heavily on volunteers, which makes it vulnerable to fluctuations in volunteer availability and commitment.
- Note: even if this is currently not an issue for this group – as noted above, the group has a committed team – this puts the group at risk for sudden labour shortages.
- This is a good example of why it is important for individuals conducting SWOT analyses to look closely at their organization, as strengths (e.g., the current team is passionate and committed to the organization’s success) can have related weaknesses (e.g., the team is mostly made up of volunteers who have other commitments that may take precedent,) and vice versa.
- Context: the group relies heavily on volunteers, which makes it vulnerable to fluctuations in volunteer availability and commitment.
The strengths and weaknesses that an advocacy group comes up with are, like the examples above, likely known by the members of the advocacy group. However, writing them down in a proper SWOT analysis provides a tangible means to address these factors and provide guidance for future strategies – either to capitalize on the organizations’ strengths or create feasible strategies to mitigate weaknesses. While not necessary, many groups find it easier to use a table when performing an internal analysis (see below) as it can make it more digestible and, thus, easier to refer to when developing future plans.